Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 02:41 am
Fairly quickly into the dissertation process, you will need to develop a conceptual framework. Perhaps second only to the purpose statement in its importance for your dissertation, the conceptual framework shapes the direction of your research. Think of it this way: if the purpose statement is your target, then the conceptual framework is the arrow that guides you to your intended target.
So how do you tackle such a critical task? Follow the steps outlined in this article to build a strong conceptual framework that will set you up for writing a successful dissertation.
Prerequisites
Before we outline the steps to building a solid conceptual framework, let’s zoom out and remind ourselves where we are in the dissertation process.
Prior to developing your conceptual framework, you will have already chosen your research topic and have developed an appropriate research question or problem statement.

Once these prerequisites are met, you are ready to move on to developing a conceptual framework for your dissertation research. Armed with a clear target (your problem statement), next you will take aim at the target by crafting a conceptual framework to effectively guide your research.
How to Create a Conceptual Framework
Step One: Conduct a literature review with your topic and problem statement in mind.
Get familiar with what is being said about your particular area of research. You probably already conducted a preliminary review of the relevant literature when you were brainstorming your topic and narrowing down your area of focus. Now take another closer look to begin noticing themes, key terms, and recurring variables mentioned in the relevant literature.
Step Two: Identify the variables affecting your problem.
Begin to jot down the themes, patterns, and variables you see emerging from the sources related to your dissertation topic. What are the independent and dependent variables of your research problem? What are the extraneous variables that impact the independent variables, such as mediating, moderating, and control variables?
Be careful here. You want to avoid going down rabbit holes chasing every possible variable. Isolate the key variables you see from the literature as most pertinent to your problem focus. Stick to a few key variables that you can discuss adequately and in an in-depth manner in your dissertation. Too many outliers muddies the waters, making for an unwieldy research process for you and confusion for your readers. Developing a clean, focused conceptual framework will help you focus on the most relevant factors.
Step Three: Identify the relationships between the key variables.

In the process of isolating the key variables impacting your research problem, you will likely have already begun to notice relationships among the variables. What are the causal relationships? What variables have a direct or indirect impact upon another variable? As mentioned in Step Two, be careful here not to chase down too many loosely connected variable relationships. You want to focus on the strongest relationships, the ones most supported by the relevant literature, and the relationships that provide the best insight into your problem statement.
Step Four: Create a visual representation of your conceptual framework.
Once you have a clear picture of the key variables of your research problem and relationships among these variables, you should be able to draw a visual flow chart of the critical components of your research. This visual represents your actual conceptual framework for your research.
The visual representation is usually a diagram, a simple flow chart with the variables in boxes and with arrows showing the flow of relationship among the variables. You could also write out the conceptual framework in outline or narrative format; however, typically a visual representation is the best way to demonstrate the relationship among your variables.
Step Five: Explain your visual representation in narrative form.

Once you have created your visual representation, explain the flow chart in a paragraph or two. This narrative of your conceptual framework will be included in your dissertation and will sum up the direction of your research. Your readers will quickly grasp the main thrust of your dissertation through this narrative description. The conceptual framework both in its chart form and in its narrative form will keep you on track over the course of your dissertation process, as well.
Simple Conceptual Framework Visual Example
This simplified flow chart provides a basic visual example of a conceptual framework for a research work seeking to analyze the key factor(s) contributing to successful second language acquisition in the classroom.
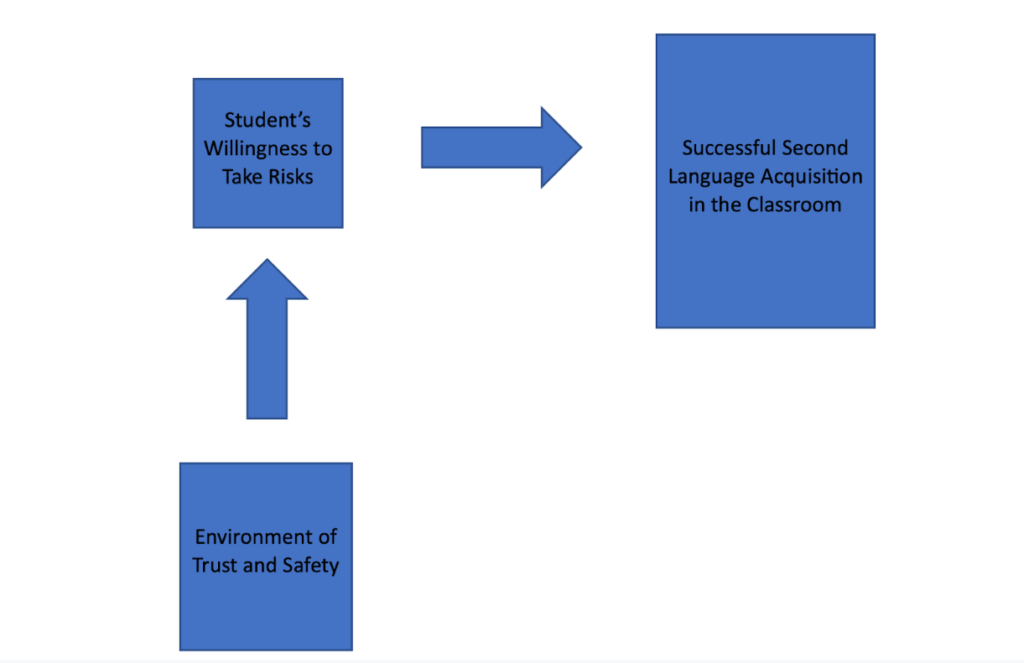
A key contributing factor to a student’s successful acquisition of a second language in a classroom setting is his or her willingness to take risks.
The control factor that ought to be provided by the teacher is the creation of a safe classroom space where enough trust has been built that students are willing to take the risks necessary in order to experiment with the second language.
The problem exists when the student does not feel safe enough to take risks in the language acquisition process, and thus does not succeed in acquiring the desired language skills.
Narrative Explanation of the Example Conceptual Framework
In the above example, we see that successful second language acquisition is the dependent variable or the desired outcome.
Student’s willingness to take risks is an important key independent variable (Other independent variables likely exist, but for example’s sake, we will limit our focus to one independent variable.)


Environment of Trust and Safety is the control variable which has a direct impact on the student’s willingness to take language risks in the classroom and thus affects the student’s success in second language acquisition. Also, this control variable is under the direct control of the classroom teacher.
Summary

A conceptual framework lends clarity to your dissertation process. It provides the guidance and structure needed to effectively write a strong dissertation.
Assessing the pertinent literature, identifying the key variables related to your problem statement, and then drawing out the relationships among the variables will lead you to the vital components of your conceptual framework. The last steps involve drawing a simple visual of your basic research components and describing that visual in a narrative format.
Follow these simple steps and writing a successful dissertation will flow naturally from your solidly constructed conceptual framework.
 Waiting to Get Your Dissertation Accepted?
Waiting to Get Your Dissertation Accepted?


